C++ PROGRAMMING
1) What is C++ ?
C++ is a general-purpose programming language developed by Bjarne Stroustrup in 1983. It extends the C programming language by introducing object-oriented features such as classes and objects, while also supporting procedural and generic programming paradigms. C++ is widely used for system/software development, game programming, and applications that require high performance due to its fine-grained control over hardware and memory.[Click Here]
.png) |
| C++ Programming |
2) Difference Between C and C++ :[video Link]
 |
| Difference Between C and C++ |
3) How To Install C++ :
How to Install C++ (GCC/G++ Compiler) on Various Platforms:
1. Windows:
Option 1: Using MinGW (Minimalist GNU for Windows)
1. Download MinGW from [MinGW Official Website](https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw/).
2. Run the installer and select "Basic Setup."
3. Select `gcc-g++` from the package list and click "Apply Changes."
4. Add the MinGW `bin` folder (usually `C:\MinGW\bin`) to your system's PATH environment variable.
5. Verify the installation by running `g++ --version` in the command prompt.
Option 2: Using Visual Studio
1. Download Visual Studio from [Microsoft's official site](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/).
2. During installation, select the "Desktop development with C++" workload.
3. Once installed, use Visual Studio to create C++ projects or compile C++ code.
2. Linux (Ubuntu/Debian-based):
1. Open the terminal.
2. Run the following commands to install the GNU C++ compiler (g++):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install g++
3. Verify the installation:
g++ --version
3. macOS:
1. Install **Xcode Command Line Tools** by running the following command in the terminal:
xcode-select --install
2. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the tools.
3. Verify the installation by running:
g++ --version
4. Using Online Compilers:
If you don't want to install anything locally, you can use online C++ compilers like:
- [Replit](https://replit.com/)
- [JDoodle](https://www.jdoodle.com/c/)
- [Compiler Explorer](https://godbolt.org/)
These platforms allow you to write, compile, and run C++ code directly in your browser.
5. Compiling a C++ Program:
After installing the compiler, you can compile a C++ program using the following command:
g++ filename.cpp -o outputname
./outputname # For Linux/macOS or outputname.exe for Windows
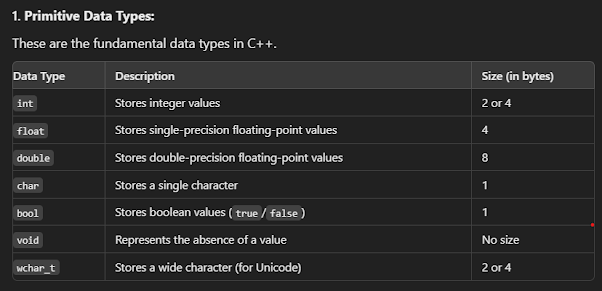
4) C++ Data Types:
5) C++ Operators :
C++ operators are classified into several types based on their functionality of the operators:
1) Arithmetic operator
2) Relational operator
3) Logical operator
4) Bitwise operator
5) Assignment operator
6) Increment and Decrement operator
7) Conditional operator
6) C++ Functions :
Functions in C++ are blocks of code that perform specific tasks and help organize code by making it reusable. A function typically consists of a return type, a name, parameters (optional), and a body that contains the code to execute.
1. Syntax of a Function:
The basic syntax of a function in C++ is as follows:
return_type function_name(parameters) {
// Function body (statements)
}
- Return Type: Indicates what type of value the function will return (e.g., `int`, `void`, `float`).
- Function Name: The identifier for the function, which is used to call it (e.g., `calculateSum`).
- Parameters: Input values passed to the function, enclosed in parentheses, and separated by commas (e.g., `int a, int b`). Parameters are optional.
- Function Body: The block of code that executes when the function is called. It is enclosed in curly braces `{}`.
- Return Statement: Ends the function's execution and optionally returns a value to the caller. The `return` statement is required if the function has a non-void return type.
2. Types of Functions in C++:
- Library Functions: These are predefined functions provided by the C++ standard library, such as `printf()`, `scanf()`, `sqrt()`, and `strlen()`. You can use these functions by including the appropriate header files.
- User-Defined Functions: These are functions created by the programmer to perform specific tasks. For example, you might define a function called `addNumbers()` to add two numbers.
3. Example of a Simple Function:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int addNumbers(int a, int b) {
return a + b; // Returns the sum of a and b
}
int main() {
int result = addNumbers(5, 3); // Function call
cout << "The sum is: " << result << endl;
return 0;
}
In this example, `addNumbers` is a user-defined function that takes two integer parameters, adds them, and returns the result. The `main` function calls `addNumbers` and prints the result.
4. Function Declaration and Definition:
- Function Declaration (Prototype): Before using a function, you can declare it to inform the compiler about its existence. This includes the return type, function name, and parameters but omits the function body. For example:
int addNumbers(int, int); // Function declaration
- Function Definition: The actual implementation of the function. It contains the function body with the code that will be executed. For example:
int addNumbers(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
5. Calling a Function:
To use a function, you simply call it by its name and pass the required arguments (if any). For example:
int result = addNumbers(10, 20);
Here, the `addNumbers` function is called with `10` and `20` as arguments, and the result is stored in the `result` variable.
Functions are a fundamental concept in C++ programming, enabling code reuse, modularity, and better organization of complex programs.












0 Comments